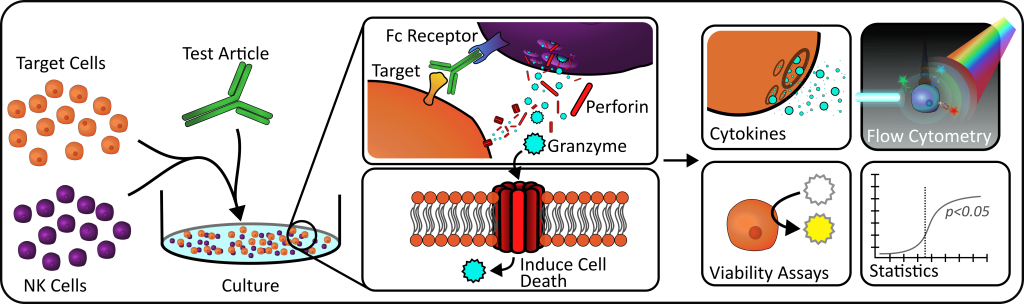
Background: Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity is a known cellular defense mechanism that employs the natural killer cells (NK) to recognize and exert cytotoxic functions on infected cells and tumors. Therapeutic antitumor monoclonal antibodies can be tested for their ADCC engagement potential. NK cells recognize and bind to the Fc portion of monoclonal antibodies (bound to target cell) and release cytotoxic granules and inflammatory cytokines that result in death of the bound target cell.
Principle: Effector cells (NK Cells) are cultured with Target Cells (cancer) in the presence of a therapeutic antibody (Test Article) to induce ADCC. Observed endpoints for ADCC include phenotyping of effector cells with activation and degranulation markers, cytokine production and cell damage (lactate dehydrogenase) or cell death.
References
Related Assays:
"*" indicates required fields
Copyright © 2021. All rights reserved.