Publication and Submission Quality Data
The final product that any CRO produces, that any client or regulatory body cares about, is the data report. Which is why Xeno Diagnostics takes just as much care with how we present the data as we do with how we perform the study. We pride ourselves on creating submission quality data tables and charts that can quickly convey the major findings. We all know that immunological data can be both complex and at times overwhelming in the sheer quantity of data, which is why it is critical that the presented information be clear, concise, and relevant.
Xeno Diagnostics scientific staff takes time to sit down with each client and discuss the results, providing interpretation by the experts who are most familiar with these assays. We will often also create custom graphics and diagrams to help explain assay concepts or critical components. Our goal is to ensure that quality data has been presented and that everyone – from scientists, project leads, investors, and regulatory bodies – can easily interpret and make actionable decisions based on the data.
Below we have compiled a number of different MLR case studies to display the type of data we routinely produce for clients. We also suggest checking out our other pages on the MLR for additional context and information on the immunological concepts behind the MLR.
Application: Assessing the immunogenicity of a therapeutic. Appropriate for Discovery and Pre-Clinical characterization of safety.
Assay Background: This assay is often considered the “gold standard” for in-vitro immunogenicity assessments. The assay uses autologous Dendritic Cells (DC’s) and T-cells (from same donor). The DC’s are preloaded with antigen (therapeutic article) and then co-cultured with T-cells to observe if indirect allorecognition occurs. The assay can be used to assess a variety of therapeutics including small molecules, antibodies, lysate from cellular therapies, and other biomaterials.
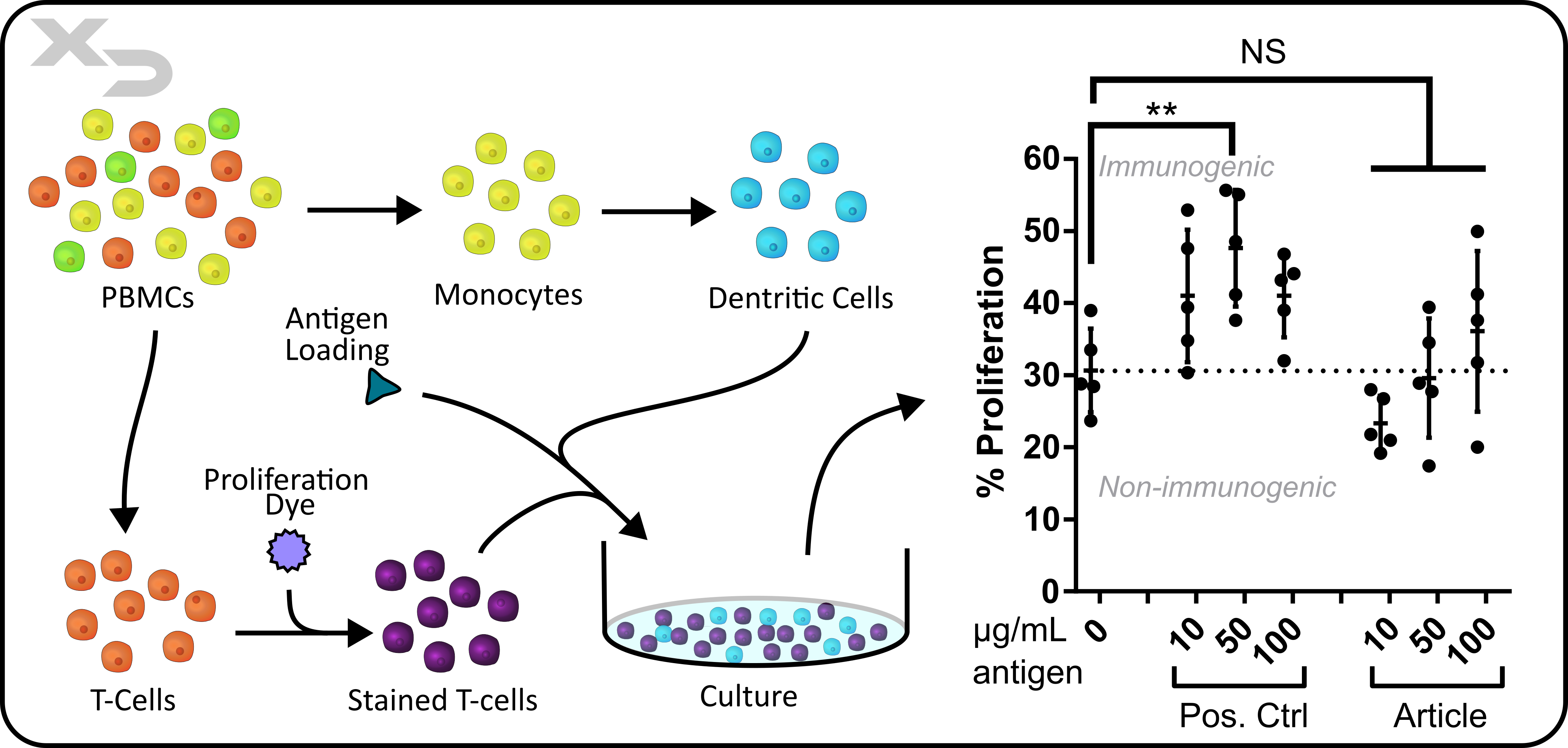
Figure: Study assessing immunogenicity of therapeutic protein (antigen). Dendritic cells (DCs) were pre-loaded with therapeutic antigen prior to culture with autologous T-cells. Articles were added at three concentrations and cultured for 7-days, after which CD4 T-cell proliferation by flow cytometry was measured. N = 5 donors, 2-way ANOVA with Dunnets multiple comparisons was performed (** p<.01).
Application: Assessing the immunomodulatory potential of a therapeutic. Appropriate for Discovery and Pre-Clinical characterization of therapeutics bioactivity, efficacy, and dose response.
Assay Background: This assay is commonly used for assessing further stimulation or inhibition of an adaptive immune response using allogeneic DC/T-cell mixed lymphocyte co-culture. The allogeneic DC/T-cell reaction produces a strong adaptive immune response, which the therapeutic may modulate. This type of assay is suited for assessing the enhancement/further stimulation (e.g. checkpoint inhibition) or testing of immunosuppressive drugs. The assay can be used to assess a variety of therapeutics including small molecules, antibodies, cellular therapies, and other biomaterials.
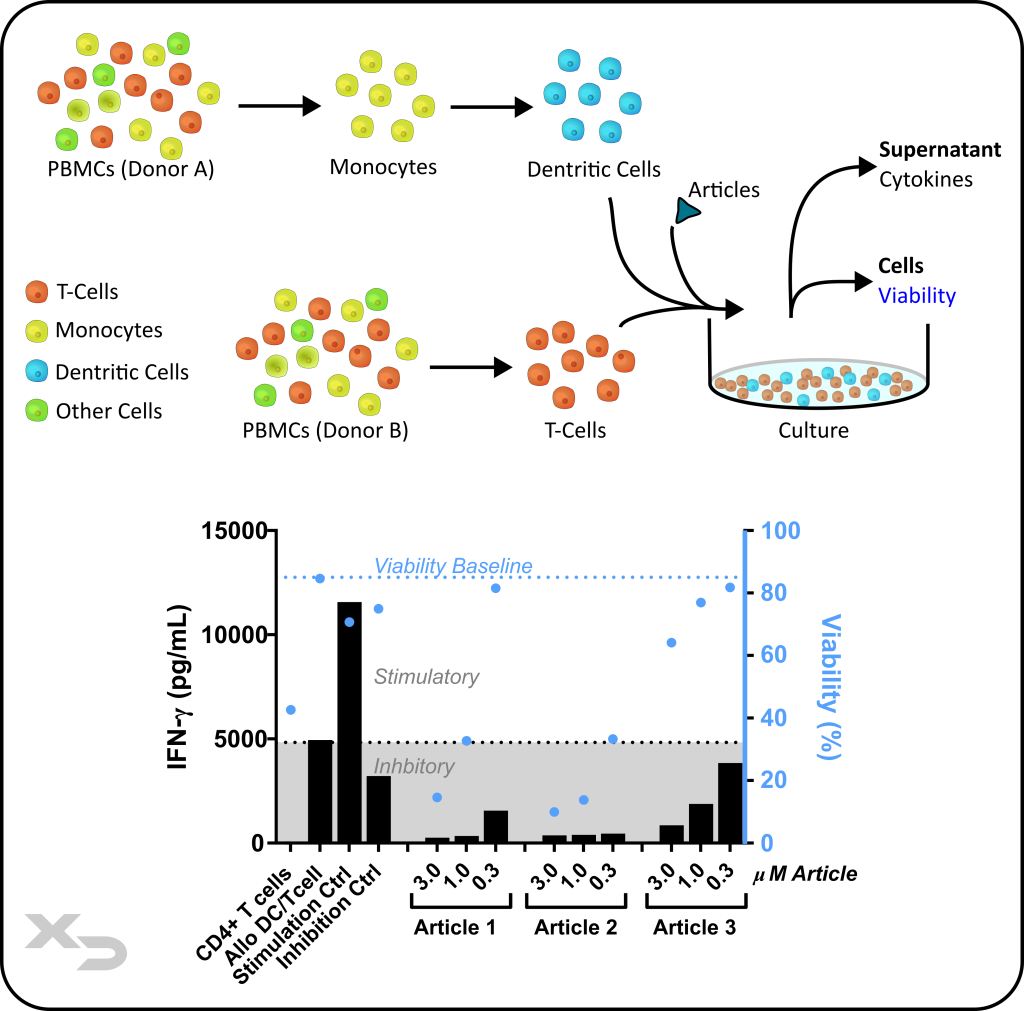
Figure: Study assessing immunosuppressive properties of potential therapeutics (articles). Dendritic cells (DCs) were cultured with allogeneic CD4 T-cells from a different donor. Articles were added at three concentrations and cultured for 6-days, after which CD4 T-cell viability is measured by flow cytometry and IFN-γ cytokine release by Luminex® MAGPIX. The data was used to assess articles and concentrations suppressing the adaptive immune response without unduly affecting viability.
Application: Assessing the immunomodulatory potential of a therapeutic. Appropriate for Discovery and Pre-Clinical characterization of a therapeutic’s bioactivity, efficacy, and dose response.
Assay Background: This assay is commonly used for assessing modulation of an adaptive immune response using allogeneic PBMCs co-cultured with the article of interest, in this case a cellular therapy. The allogeneic reaction between PBMC donors produces a strong response which can be altered by the cellular therapy (either via enhancement or inhibition). The one-way MLR allows for only a single PBMC donor to respond, perfect for global analysis methods like BrdU ELISA or cytokine analysis.
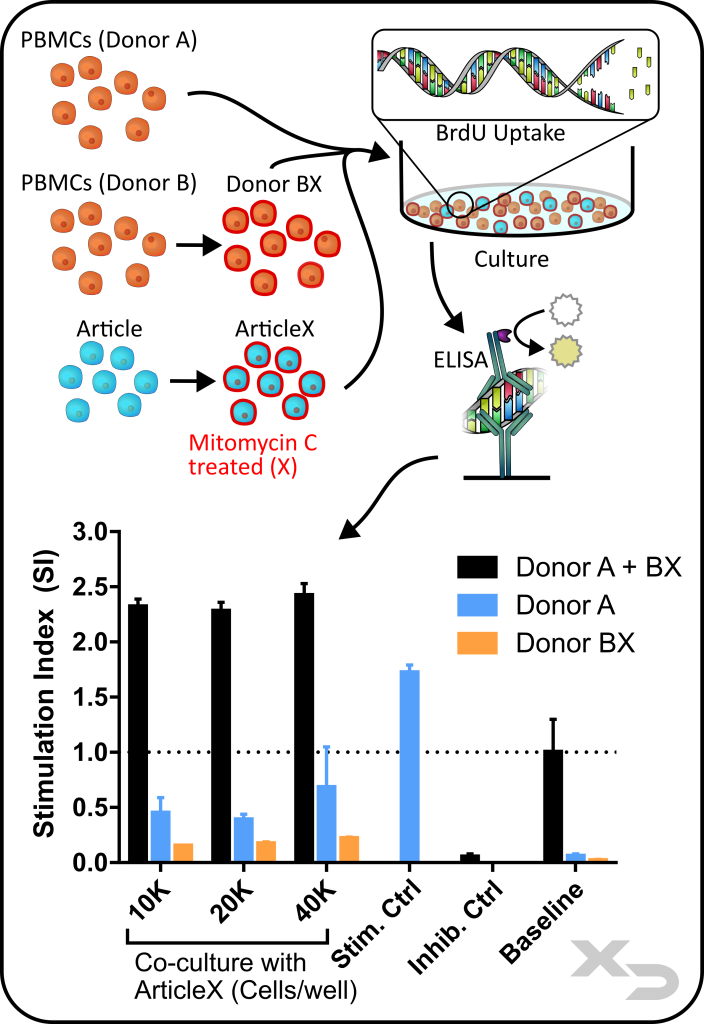
Figure: Study assessing immunomodulatory properties of cellular therapies (articles). PBMCs from two different donors (A and B) were co-cultured with cellular therapy at multiple concentrations. PBMCs from one donor and the cellular therapy were treated with mitomycin c (X) to arrest proliferative responses. Proliferation a single PBMC donor was performed by BrdU ELISA.
Application: Assessing the immunomodulatory potential of a therapeutic. Appropriate for Discovery and Pre-Clinical characterization of therapeutics bioactivity, efficacy, and dose response.
Assay Background: This assay is commonly used for assessing the modulation of an adaptive immune response using allogeneic PBMCs co-cultured with the article of interest, in this case an antibody therapeutic. The allogeneic reaction between PBMC donors produces a strong response which the cellular therapy can modulate (either via enhancement or inhibition).
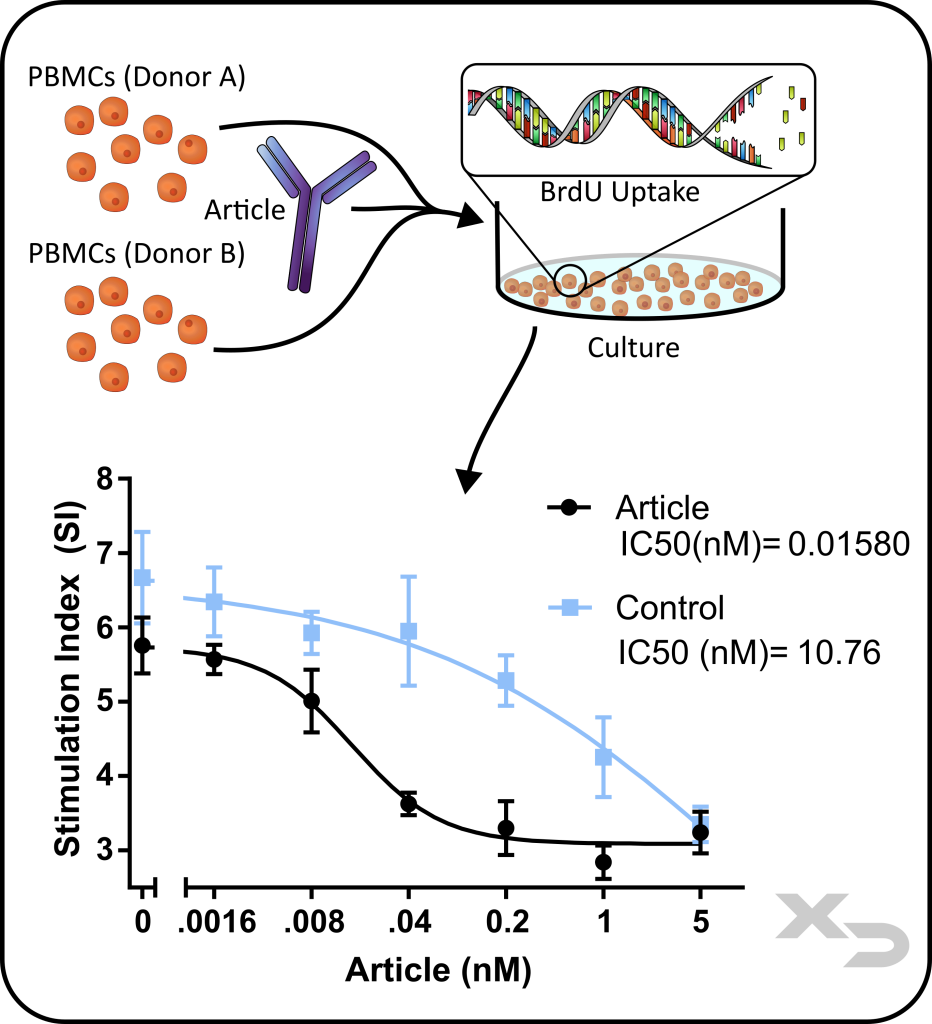
Figure: Study assessing immunomodulatory properties of antibody therapy (articles). PBMCs from two different donors (A and B) were co-cultured with antibody at multiple concentrations. Proliferation was performed by BrdU ELISA, stimulation index was calculated and IC50 concentrations determined.
Application: Assessing the immunogenicity of a therapeutic. Appropriate for Discovery and Pre-Clinical characterization of a therapeutic’s bioactivity/immunogenicity.
Assay Background: This assay is commonly used for assessing the activation of an adaptive immune response using autologous PBMCs co-cultured with the article of interest, in this case bone matrix material. The immunogenic reaction is initiated by both indirect allorecognition (foreign antigen processing by APCs to display to autologous T-cells) and direct allorecognition (foreign MHC I receptors on bone matrix mismatch with PMBC CD8 TCR).
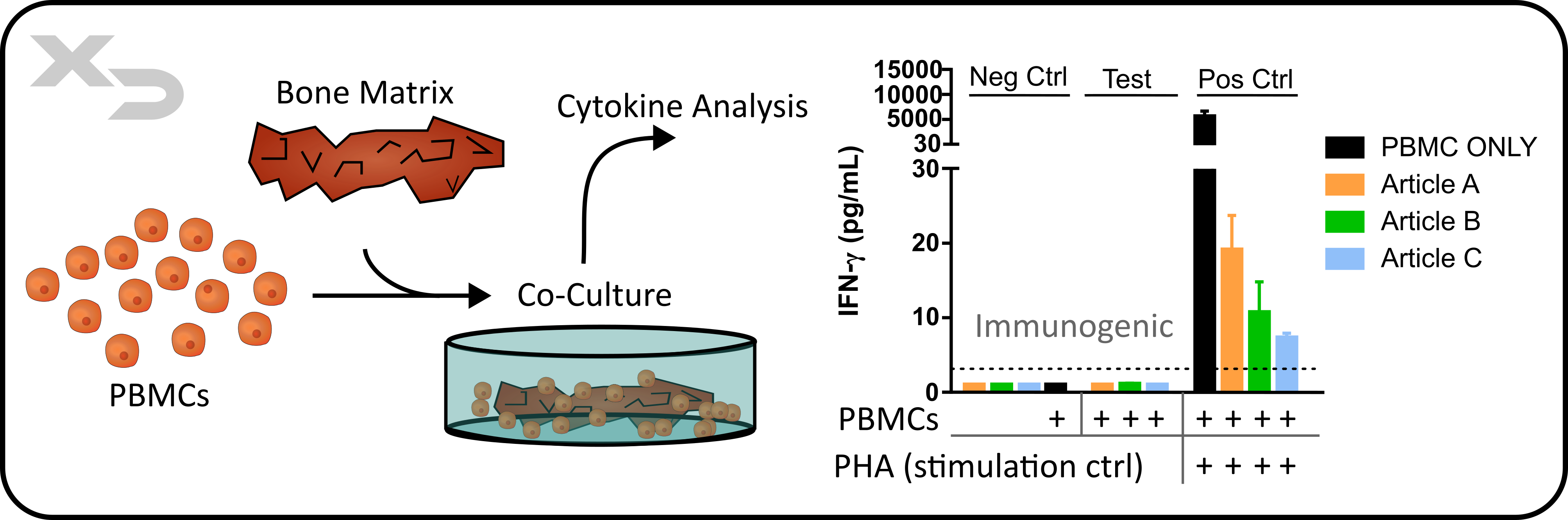
Figure: Study assessing immunogenic properties of bone matrix therapeutic (articles). PBMCs from a single donor were co-cultured with three articles for four days, after which T-cell viability (not shown) IFN-γ cytokine release was measured. Notably, the bone matrix articles not only showed no immunogenicity when cultured with PBMCs, but when a positive control stimulus (PHA) was added, the articles suppressed the immune response.
MLR’s model an adaptive immune response:
Want to know the immunological concepts behind the MLR? Checkout our webpage which discusses the minutia of cell-mediated immunity and how the MLR leverages those concepts to provide an informative assay.
Analyzing MLR’s:
Decades of cell biology and immunological research have given us countless ways to measure and analyze a cellular response. At Xeno Diagnostics we use every technique at our fingertips. Absorbance, fluorescence, luminescence; ELISAs, Flow Cytometry, PCR, and more. Cells are complex and can respond in a myriad of different ways, so it only makes sense that we employ multiple strategies to assess as much as possible. Our Expert Team can pair multiple readouts for data-rich results, or hone in on the most critical factors with single readouts. Whether it’s for lot release, potency, or mechanism of action, we can get you the results you need.
MLR Solutions For Industry Guidance:
MLR is a powerful tool for immunological research and can be a critical asset in many drug development pipelines. From Discovery to Pre-Clinical and Clinical Studies; no matter where you are in the process Xeno Dx has an MLR service to help you!
MLRs Are Adaptive:
MLRs replicate our adaptive immune system via cell-cell mediated interactions. But just like our immune system, it is more complex than that. Cell interactions can be autologous (indirect allorecognition) or allogeneic (direct allorecognition). They can involve purified cells (e.g. DC/Tcell format) or they can use mixed populations (e.g. PBMCs). Cells can be from one donor or multiple, or different species. Each variation serves a different purpose and can be used to investigate different aspects of a therapeutic product’s immunological effects. Let us help you pick out which MLR is right for you!
"*" indicates required fields
Copyright © 2021. All rights reserved.