The mixed lymphocyte tumor cell (MLTuC), also called the mixed lymphocyte tumor reactivity (MLTR) assay, has been used to determine the immune reactivity of a patient’s lymphocytes with tumor cells from the same individual (autologous). The MLTuC assay was first described by Stjernsward et al. (1970) and was based on the mixed lymphocyte response (MLR) method. The MLTuC assay is conducted to determine either 1) the induction of primary immune responses to tumor-associated cell-surface antigens, or 2) is there pre-existing cell-mediated immunity from prior exposure to these antigens.
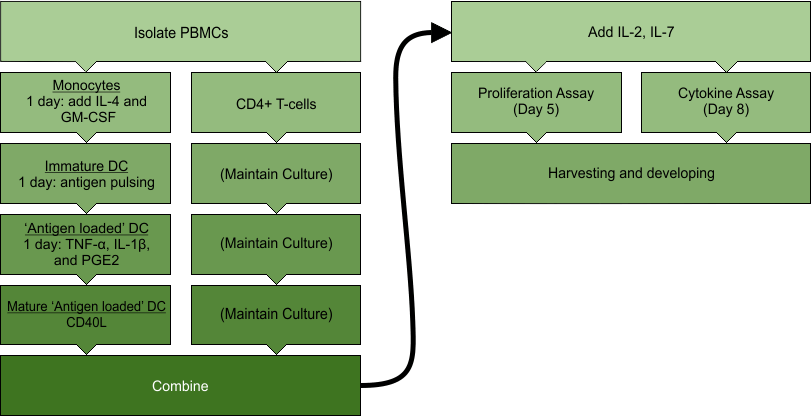
More recently, research has been conducted with the MLTuC method in attempts to generate T-lymphocytes that are cytotoxic to specific tumor cell types. However, culturing primary T-lymphocytes with most tumor cell types results in generally weak anti-tumor activity. A more successful approach is one where the tumor cell antigens are presented to T-lymphocytes in culture via the addition of autologous dendritic cells that have been pre-loaded with the tumor antigens of interest (cross-priming).
References:
Stjernsward J, Almgard LE, Franzen S, Von Schreeb T and Wadstrom LB (1970). Tumor-distinctive cellular immunity to renal carcinoma. Clin Exp Immunol 6: 963-668. PMID:5477730
Uchida A, Moore M and Klein E (1988). Autologous mixed lymphocyte-tumor reaction and autologous Mixed Lymphocyte Reaction. II. Generation of specific and non-specific killer T cells capable of lying autologous tumor. Int J. Canc 41: 651-656. PMID:2966771
Montagna D, Maccario R, Locatelli F, Rosti V, Yang Y, Farness P, Moretta A and Comoli P (2001). Ex vivo priming for long-term maintenance of antileukemia human cytotoxic T cells suggests a general procedure for adoptive immunotherapy. Blood. 98:3359-3366. PMID:11719375
Canderan G, Gruarin P, Montagna D, Fontana R, Melloni G, Traversari C, Dellabona P and Casorati G (2010). An efficient strategy to induce and maintain in vitro human T cells specific for autologous non-small cell lung carcinoma. PLos ONE 5(8): e12014. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0012014. PMID:20711505
Copyright © 2021. All rights reserved.